Introduction: The Economic Transformation of the Energy Age
The twenty-first century marks a pivotal turning point in human history — a transformation not merely technological but economic and civilizational. The shift from fossil-fuel dependence to a green energy ecosystem is triggering what many economists call the Fourth Industrial Revolution of Energy. This transformation is rewriting the logic of global capitalism, redefining national competitiveness, and reshaping the very geography of power.
Unlike previous energy transitions — from wood to coal, coal to oil, and oil to electricity — today’s transformation is intentional. It is driven not by scarcity, but by sustainability; not by market convenience, but by existential necessity. Climate change, volatile oil prices, and geopolitical tensions have forced nations to reimagine their energy futures. Green energy is no longer a niche market — it is the economic backbone of the coming decades.
1. The Macroeconomic Imperative: Decarbonization as Growth Strategy
1.1 From Environmental Cost to Economic Catalyst
For much of the 20th century, environmental protection was viewed as a constraint on growth — a moral necessity but an economic burden. That equation has now flipped. The green transition has become the new engine of innovation, investment, and employment.
Global investment in renewable energy surpassed $1.8 trillion in 2023, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA), exceeding combined fossil fuel exploration spending for the first time in history. Meanwhile, the cost of renewable electricity from solar and wind has fallen by more than 80% since 2010, making it cheaper than coal in most markets.
This inversion — where sustainability and profitability align — represents a structural shift in the global economy. The green energy sector is now a major growth driver, supporting new industries in battery manufacturing, hydrogen production, grid infrastructure, and digital energy management.
1.2 Climate Policy as Industrial Policy
Decarbonization is no longer merely an environmental goal; it is an industrial strategy. Governments are deploying massive subsidies, tax incentives, and trade frameworks to capture a share of the emerging clean-energy economy.
- The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) allocates over $369 billion to renewable energy, electric vehicles, and clean manufacturing.
- The European Union’s Green Deal sets legally binding carbon neutrality goals by 2050, alongside a €600 billion investment plan for green technologies.
- China’s 14th Five-Year Plan integrates renewables, nuclear expansion, and large-scale grid modernization into its economic growth blueprint.
The race is not simply to reduce emissions — but to dominate the technologies of the future: photovoltaics, batteries, electric vehicles, hydrogen, and smart grids.
2. The Structure of the Global Green Energy Market
2.1 Renewable Generation and Market Share
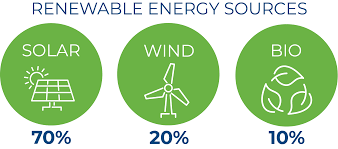
In 2024, renewables accounted for over 30% of global electricity generation, a figure expected to surpass 50% by 2030. Solar power is leading this charge, followed by wind and hydro.
China dominates manufacturing, producing more than 80% of global solar modules and over half of wind turbine components. The European Union, Japan, and South Korea lead in energy efficiency technologies and hydrogen systems, while the United States focuses on digital grid management and advanced storage.
2.2 The Energy Value Chain: From Raw Materials to Data
The green energy economy spans a complex value chain that extends from critical minerals extraction to digital energy analytics.
- Raw Materials — Lithium, cobalt, and rare earths are essential for batteries and turbines. Their global supply chain is heavily concentrated, creating strategic dependencies.
- Component Manufacturing — Asia currently dominates production capacity, but new regionalization trends are emerging in North America and Europe.
- Energy Infrastructure — Installation of solar farms, wind parks, and hydrogen facilities is now one of the largest sources of global infrastructure spending.
- Digital Integration — AI and IoT systems optimize energy flows, predictive maintenance, and smart-grid balancing, merging the digital and physical energy economies.
2.3 Green Finance and the Rise of ESG Capital
Financial markets have become a decisive force in accelerating the energy transition. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) funds now manage over $40 trillion globally, directing capital away from carbon-intensive assets.
Green bonds, sustainable infrastructure funds, and climate-linked securities are reshaping investment behavior. In parallel, central banks — from the European Central Bank to the People’s Bank of China — are integrating climate risk into monetary policy, signaling a fundamental revaluation of what constitutes economic stability.
3. Industrial Transformation: The Rebirth of Energy-Intensive Sectors
3.1 Electrification and the New Industrial Paradigm
Industries that once symbolized pollution — steel, cement, and chemicals — are now at the frontier of decarbonization. The electrification of industry, powered by renewables, is redefining manufacturing economics.
In Sweden, projects like HYBRIT and H2 Green Steel are using hydrogen-based processes to produce zero-carbon steel. In the United States, carbon capture and storage (CCS) is being integrated into petrochemical plants. Meanwhile, green ammonia derived from renewable hydrogen is emerging as both fertilizer and maritime fuel.
This transformation goes beyond environmental compliance — it is a race for technological leadership. The firms that decarbonize fastest will control tomorrow’s markets.
3.2 The Role of Automation and AI
Automation and digitalization are amplifying the efficiency gains of renewable technologies. AI algorithms forecast demand, optimize energy dispatch, and manage grid dynamics in milliseconds. Digital twins simulate energy systems to reduce waste and predict maintenance needs.
The fusion of Industry 4.0 with the green economy — often referred to as Industry 5.0 — creates smart factories that are both productive and sustainable. Energy becomes not just a cost but a competitive differentiator.

4. Energy Geopolitics: From Oil Wars to Tech Wars
4.1 A Shift in Global Power
The fossil-fuel era was defined by control over oil reserves; the green energy era will be defined by control over technology and materials. The geopolitical map is being redrawn.
Oil-exporting nations like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are diversifying aggressively into solar and hydrogen projects, while resource-rich countries such as Chile, Australia, and Indonesia are positioning themselves as the new energy suppliers through lithium and nickel exports.
Meanwhile, technological superpowers — the U.S., China, and the EU — compete for leadership in semiconductors, batteries, and AI-driven energy systems. Control of intellectual property has replaced control of pipelines as the new instrument of influence.
4.2 Strategic Dependencies and Supply Chain Security
As the global demand for critical minerals surges, supply chain security has become a national priority. The EU’s Critical Raw Materials Act, the U.S. Defense Production Act allocations for battery materials, and China’s export controls on rare earths all reflect this new form of energy nationalism.
International collaboration, however, remains vital. No single country can monopolize all materials, technologies, and innovation ecosystems needed for a full green transition. Multilateral frameworks such as the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) and the Clean Energy Ministerial aim to coordinate sustainable sourcing and technology sharing.
5. The Global South: Inclusion, Justice, and Development
5.1 Energy Access as Human Right
Over 750 million people worldwide still lack access to electricity, most in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. The green energy revolution offers a historic opportunity to close this gap without repeating the carbon-intensive path of industrialized nations.
Decentralized solar systems, mini-grids, and bioenergy projects can bring power to remote communities more cheaply and sustainably than conventional grids. Yet financing remains a major barrier — only 2% of global clean-energy investment currently reaches Africa.
5.2 Green Colonialism and Fair Transition
Critics warn of a new form of “green colonialism,” where resource extraction for clean technologies replicates the exploitative patterns of the fossil era. True sustainability demands ethical supply chains, fair labor practices, and local value creation.
Organizations such as the African Renewable Energy Initiative (AREI) and the Global Green Hydrogen Alliance are working to ensure that developing nations become not just suppliers of materials but participants in manufacturing, innovation, and ownership.
6. Employment, Skills, and the Human Capital Transition
6.1 The Green Job Revolution
The ILO estimates that the green economy could create up to 30 million new jobs globally by 2030, outpacing losses in fossil sectors. New occupations are emerging across fields: solar technicians, battery engineers, hydrogen chemists, carbon accountants, and data-driven energy analysts.
6.2 Workforce Reskilling
However, this transition also demands massive workforce reskilling. Fossil-dependent regions require retraining programs and social safety nets. The EU’s Just Transition Fund and the U.S. Energy Communities Initiative exemplify policies designed to support displaced workers while fostering new skill ecosystems.
7. Finance, Innovation, and the Role of the Private Sector
Private enterprise drives most green innovation. Startups and established corporations alike are competing to redefine the economics of sustainability.
- Tesla and BYD are transforming transportation through battery innovation.
- Ørsted has transitioned from a fossil energy giant to a global wind power leader.
- NextEra Energy in the U.S. is now the world’s largest generator of renewable electricity.
Venture capital funding for climate-tech startups surpassed $70 billion in 2024, spanning sectors from carbon removal to smart materials. Meanwhile, corporate sustainability reporting is becoming mandatory in major markets, embedding climate accountability into business DNA.
8. Barriers and Bottlenecks in the Green Transition
8.1 Infrastructure and Intermittency
The integration of intermittent renewables into existing grids remains technically and financially demanding. Energy storage capacity must expand tenfold by 2035 to meet stability needs.
8.2 Policy Fragmentation
Inconsistent regulations, slow permitting, and trade barriers delay projects and inflate costs. Harmonizing international standards is essential for scaling deployment and innovation.
8.3 Capital Inequality
Developing nations face higher borrowing costs and weaker financial institutions, limiting their ability to invest in green infrastructure. Bridging this green finance gap is the defining challenge of global climate equity.
Conclusion: The New Logic of Prosperity
The global green energy economy is more than an industrial transformation — it is a redefinition of prosperity itself. In the 20th century, wealth was measured by how much energy a nation could extract; in the 21st, it will be measured by how efficiently it can generate, store, and share it.
The nations and companies that lead in clean technologies will not only dominate markets but also define the moral and ecological narrative of human progress. The transition will be uneven, contested, and complex, but its trajectory is irreversible.
In the emerging world order, green energy is the new currency of power, and sustainability is the true measure of success.