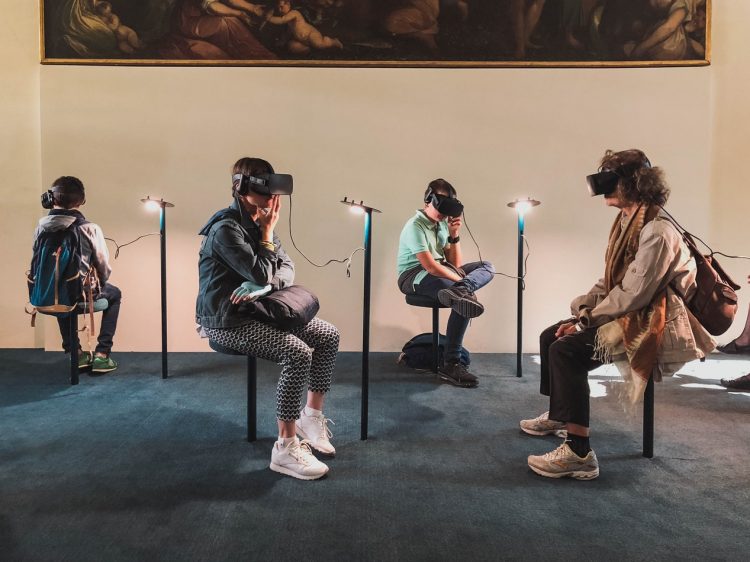
Virtual reality (VR) has come a long way since its inception in the mid-20th century. What was once a niche technology primarily used for gaming and entertainment has rapidly expanded into various sectors of life, creating immersive experiences that are reshaping industries like healthcare, education, and social networking. However, one of the most exciting developments in the world of VR is the emergence of the Metaverse — a fully immersive, persistent virtual universe that is poised to transform how we live, work, and interact in the digital age.
In this article, we will explore how VR has evolved beyond gaming into a powerful tool for creating new types of social, professional, and economic experiences. We will delve into the concept of the Metaverse, examining its current state, the technologies that drive it, and what the future may hold for this digital frontier. VR is no longer just an entertainment medium; it is becoming the fabric of an entirely new virtual reality, one where users can live, socialize, shop, work, and create in ways that were once unimaginable.
The Evolution of VR: From Video Games to Social Interaction
VR technology was initially introduced in the 1990s as a tool for enhancing gaming experiences. Early VR systems, such as those used in arcade games or theme parks, offered limited interactivity and required bulky headsets and peripherals. Despite the excitement surrounding these early experiments, VR struggled to break into the mainstream due to its high cost, lack of content, and the technological limitations of the time.
However, the advent of smartphones, high-definition displays, and more powerful processors helped to spark a new wave of VR innovation in the mid-2010s. Companies like Oculus VR, HTC Vive, and Sony PlayStation VR released consumer-ready headsets that were more affordable and accessible than ever before. These headsets, combined with motion-tracking controllers and immersive software, enabled gamers to experience fully interactive worlds where they could see, move, and interact with objects and characters in a three-dimensional space.
Gaming remained the primary driver of VR adoption, and for good reason. Video games have always been at the forefront of pushing the boundaries of new technologies, and VR offered an entirely new way to experience immersive virtual worlds. Games like Beat Saber, Half-Life: Alyx, and No Man’s Sky VR provided players with unprecedented levels of immersion and interaction. As the gaming industry embraced VR, it helped pave the way for its expansion into other fields, including social media, education, and even business.
The Metaverse: A New Digital Universe
The concept of the Metaverse has gained significant attention in recent years, particularly with companies like Facebook (now Meta) leading the charge. The Metaverse is often described as a collective virtual space made up of interconnected digital environments where people can socialize, work, create, and engage with each other in real-time. It represents the convergence of virtual reality, augmented reality (AR), and the Internet, creating an all-encompassing digital ecosystem that mirrors and expands upon the physical world.
In the Metaverse, users can create avatars to represent themselves in virtual spaces. These avatars can interact with others, participate in events, visit virtual shops, attend conferences, or even live out entire parallel lives. Companies like Meta, Google, Microsoft, and Epic Games are investing heavily in building the Metaverse, with the aim of creating a persistent, open digital world that integrates seamlessly with everyday life.
One of the key driving forces behind the Metaverse is the notion of virtual economy — a thriving marketplace where users can buy, sell, and trade digital goods and services. For instance, in games like Second Life and Decentraland, players can purchase virtual land, clothing, and accessories for their avatars, creating a thriving digital marketplace. Additionally, virtual currencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are increasingly being used within Metaverse platforms, giving rise to new forms of commerce and economic opportunities.
VR in Social Networking: Creating New Virtual Spaces
As we continue to move toward the Metaverse, the role of VR in social networking is becoming more prominent. Traditional social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter are largely built around text, images, and videos. These platforms are designed for one-way communication, where users share content, and others engage with it in a passive manner.
Virtual reality, however, offers a more immersive form of interaction. In VR, users can engage in real-time 3D experiences where they are represented by avatars in a shared space. This allows for synchronous communication, where people can interact with each other in ways that feel more natural and social, much like face-to-face interaction. VR platforms like AltspaceVR, VRChat, and Rec Room have already established virtual social spaces where people can meet, attend events, play games, or simply hang out.
These virtual social networks go beyond the limitations of traditional social media by allowing users to express themselves in more creative ways. Avatars in VR can be highly customizable, allowing individuals to design their virtual selves to reflect their personalities or experiment with different identities. Users can also engage in activities like virtual reality concerts, art exhibitions, and meetups, creating a richer social experience that feels less detached than scrolling through a feed of images and status updates.
As more people embrace these virtual spaces, it is possible that VR social networks could become the dominant form of online interaction. The Metaverse promises to further blur the boundaries between physical and digital social experiences, offering new opportunities for global connection, collaboration, and cultural exchange.
The Economic Implications of the Metaverse
The rise of the Metaverse presents both exciting opportunities and challenges from an economic standpoint. As virtual reality continues to evolve, entire new markets and industries are emerging, and traditional business models are being disrupted. Some of the key areas where VR is making an economic impact include:
Virtual Real Estate
One of the most intriguing aspects of the Metaverse is the concept of virtual real estate. As more virtual worlds are created, there is a growing demand for virtual spaces where users can live, work, and interact. Platforms like Decentraland and Somnium Space have created virtual environments where users can purchase digital land and build on it. These virtual properties can be used for a variety of purposes, such as hosting events, running businesses, or simply creating spaces for social interaction.
Just like the physical real estate market, virtual land in the Metaverse is bought and sold for profit. This has given rise to a new form of virtual property investment, where individuals and companies buy up parcels of virtual land with the expectation that their value will increase as the Metaverse grows. While virtual real estate is still a relatively new concept, it has already attracted significant investment, and experts predict that it could become a $1 trillion industry within the next decade.
Digital Goods and Services
In the Metaverse, users can purchase digital goods such as clothing, accessories, and even furniture for their avatars and virtual spaces. These digital items are often bought with cryptocurrency, which is becoming the standard currency for transactions within virtual worlds.

This rise of digital commerce is enabling a new wave of virtual businesses. Designers, developers, and artists can sell virtual items to users across multiple Metaverse platforms, creating new revenue streams and business opportunities. Virtual fashion, in particular, has emerged as a burgeoning industry, with companies like Gucci, Nike, and Balenciaga launching virtual collections for avatars. This shift in how we perceive value and ownership could have long-term implications for industries like retail, entertainment, and advertising.
Jobs and Remote Work in the Metaverse
As the Metaverse expands, it is also reshaping the way people work. Virtual reality offers new opportunities for remote collaboration and job creation. Businesses are already adopting virtual offices where employees can meet in shared digital environments, conduct meetings, and collaborate on projects without leaving their homes.
This virtual workspace is not limited to office jobs; creators and developers can collaborate on building virtual worlds or even host virtual concerts and conferences. In the future, the Metaverse could become the default platform for remote work, providing global teams with access to a shared virtual space.
The Future of VR: Towards a Fully Immersive Digital World
The future of virtual reality is undoubtedly intertwined with the evolution of the Metaverse. As VR technology improves, the Metaverse will become more immersive and accessible. We can expect to see advancements in haptic feedback, eye tracking, and brain-computer interfaces that will make virtual experiences feel more realistic and interactive.
With the growth of 5G networks and advances in cloud computing, we can also expect VR experiences to become more seamless, with higher-quality graphics, reduced latency, and more engaging interactions.
However, the Metaverse also raises important ethical and societal questions. As people spend more time in virtual environments, concerns around privacy, identity, and social isolation will need to be addressed. The boundaries between reality and virtuality may blur, raising questions about how we maintain a healthy balance between the two.
Despite these challenges, the Metaverse is poised to become one of the most significant technological innovations of the next decade. From gaming to social networking, from commerce to education, the Metaverse promises to offer entirely new forms of experience and interaction, bringing us closer to a fully integrated digital world.