Introduction: The Urgency of Climate Action
Climate change is one of the most pressing challenges of the 21st century. Rising global temperatures, melting ice caps, extreme weather events, and sea-level rise threaten ecosystems, economies, and human societies. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) warns that unless immediate and substantial mitigation measures are implemented, the consequences will be catastrophic and irreversible.
Climate change mitigation involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing carbon sinks to limit global warming. This article explores mitigation strategies across energy, transportation, industry, urban planning, agriculture, policy frameworks, and societal engagement, providing a roadmap for a sustainable future.
1. Energy Sector Transformation
1.1 Transition to Renewable Energy
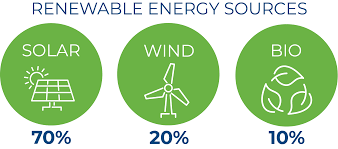
The energy sector accounts for approximately 73% of global greenhouse gas emissions, making decarbonization essential. Renewable energy solutions include:
- Solar energy: Rooftop PV systems, solar farms, and concentrated solar power
- Wind energy: Onshore and offshore turbines with high efficiency
- Hydropower: Small and large-scale hydroelectric plants
- Bioenergy: Sustainable biomass for heat and power
Countries like Germany, China, and Denmark have significantly expanded renewable energy capacity, demonstrating economic viability and environmental benefits.
1.2 Energy Efficiency
Reducing energy demand is equally important. Strategies include:
- High-efficiency appliances and lighting
- Insulation and energy-efficient building design
- Industrial process optimization
Improved efficiency can reduce emissions by up to 30% in some sectors, lowering both costs and environmental impact.
1.3 Grid Modernization and Energy Storage
Smart grids and advanced energy storage enable integration of intermittent renewables. Benefits include:
- Load balancing and demand response
- Reduced reliance on fossil fuel backup
- Enhanced resilience to power outages
Energy storage technologies, including lithium-ion and emerging solid-state batteries, are critical for a renewable-powered future.
2. Sustainable Transportation Solutions
2.1 Electrification of Mobility
Transportation contributes roughly 14% of global emissions. Electrification reduces reliance on petroleum-based fuels:
- Electric cars, buses, and trucks
- Integration with renewable energy for charging
- Development of charging infrastructure in urban and rural areas
Cities like Oslo and Amsterdam showcase successful electric vehicle adoption through incentives, infrastructure, and policy support.
2.2 Public Transportation and Active Mobility
Shifting from private cars to public and active transportation reduces emissions and congestion:
- Metro, tram, and bus rapid transit systems
- Bicycle lanes and pedestrian-friendly urban planning
- Integrated multimodal transport networks
Combining electrification with public transport maximizes emissions reduction.
2.3 Aviation and Shipping Innovations
Long-distance transport is harder to decarbonize. Innovations include:
- Sustainable aviation fuels (SAF)
- Electric and hybrid aircraft
- Low-emission shipping technologies
International cooperation and regulation are essential for decarbonizing these sectors.
3. Industrial and Manufacturing Mitigation
3.1 Cleaner Production Technologies
Industries are responsible for about 21% of emissions. Mitigation strategies include:
- Electrification of industrial processes
- Carbon capture and storage (CCS)
- Process optimization using AI and IoT
3.2 Circular Economy Approaches
Reducing material use and recycling can lower industrial emissions:
- Resource-efficient manufacturing
- Waste-to-energy and recycling programs
- Sustainable supply chain management
Companies adopting circular strategies achieve both environmental and economic benefits.
4. Urban Climate Strategies
4.1 Green Building Design
Buildings contribute significantly to emissions. Sustainable building strategies include:
- Passive design and natural ventilation
- Energy-efficient HVAC systems
- Renewable energy integration
Green building certifications, such as LEED and BREEAM, guide sustainable construction practices.

4.2 Urban Planning and Green Spaces
Compact, mixed-use neighborhoods and green infrastructure:
- Reduce transport emissions
- Mitigate urban heat islands
- Enhance air quality and human well-being
Examples include Singapore’s vertical greenery and Copenhagen’s bicycle network, integrating climate adaptation with emission reduction.
4.3 Waste Management
Proper waste management reduces methane emissions from landfills:
- Recycling and composting
- Waste-to-energy conversion
- Circular urban industrial practices
Waste management is an often-overlooked yet critical component of urban climate strategy.
5. Agriculture, Forestry, and Land Use
5.1 Sustainable Agriculture
Agriculture emits both CO2 and methane. Sustainable practices include:
- Precision farming to reduce fertilizer use
- Crop rotation and agroforestry
- Conservation tillage and soil carbon sequestration
5.2 Forest Conservation and Reforestation
Forests act as vital carbon sinks. Strategies include:
- Preventing deforestation and illegal logging
- Community-led reforestation projects
- Protecting peatlands and mangroves
Projects like Brazil’s Amazon protection initiatives demonstrate the impact of forest conservation on global emissions.
5.3 Climate-Smart Land Use Planning
Integrated land management balances agricultural, urban, and natural needs:
- Zoning and land-use regulation
- Ecosystem restoration
- Bio-diverse and resilient landscapes
Effective land use reduces emissions while supporting food security and biodiversity.
6. Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)
6.1 Carbon Capture Technologies
CCUS captures CO2 from industrial processes or directly from the air:
- Post-combustion capture from power plants
- Direct air capture (DAC) technologies
- Mineralization and long-term geological storage
6.2 Carbon Utilization
Captured carbon can be converted into:
- Building materials, fuels, and chemicals
- Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) with caution for lifecycle emissions
- Sustainable plastics and composites
CCUS complements renewable energy and efficiency measures to achieve net-zero emissions.
7. Policy, Regulation, and Global Cooperation
7.1 International Agreements
Climate treaties like the Paris Agreement set global targets to limit warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. Key mechanisms:
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
- Carbon markets and emissions trading
- Climate finance for developing nations
7.2 National and Local Policies
Countries implement mitigation strategies tailored to context:
- Carbon taxes and subsidies for clean energy
- Regulations on industrial emissions and vehicle efficiency
- Urban climate action plans integrating multiple sectors
7.3 Role of Civil Society and Private Sector
Businesses and NGOs drive innovation and accountability:
- Corporate sustainability commitments
- Public-private partnerships for renewable energy projects
- Advocacy and citizen engagement in policy development
8. Social and Behavioral Dimensions
8.1 Education and Awareness
Public understanding of climate science and mitigation strategies is vital:
- School and university programs
- Media campaigns on sustainable practices
- Community workshops and participatory projects
8.2 Lifestyle and Consumption Changes
Individuals contribute by:
- Reducing energy consumption
- Choosing low-carbon transportation
- Supporting sustainable products and services
Collective action amplifies impact, complementing technological and policy measures.
9. Technological Innovation and Research
9.1 Renewable Energy Advancements
Next-generation technologies include:
- Floating offshore wind turbines
- High-efficiency photovoltaic materials
- Grid-scale battery storage systems
9.2 Artificial Intelligence and IoT
AI and IoT optimize emissions reduction across sectors:
- Smart grid management
- Precision agriculture
- Traffic and logistics optimization
9.3 Emerging Carbon Removal Technologies
Innovations such as enhanced weathering, biochar, and ocean-based carbon removal expand mitigation pathways beyond conventional methods.
10. Challenges and Future Directions
Despite progress, mitigation faces obstacles:
- Unequal access to clean technology
- Political resistance and fossil fuel dependency
- Financial constraints for developing countries
- Coordination challenges across sectors and nations
Future mitigation strategies must integrate technology, policy, finance, and social engagement to achieve scalable and equitable impact.
Conclusion: Building a Sustainable Future
Climate change mitigation is both urgent and complex. It requires coordinated action across energy, transport, industry, agriculture, urban planning, and society.
The combination of renewable energy, energy efficiency, smart urban planning, carbon management, and behavioral change offers a viable path to a sustainable future. International cooperation, innovation, and citizen engagement are essential to meet global targets and ensure a resilient planet.
Mitigation is not merely a technical challenge; it is a moral and societal imperative. By embracing comprehensive strategies, humanity can limit climate risks, protect ecosystems, and secure a sustainable legacy for future generations.